Proactive Resilience: Creating an IT Disaster Recovery Plan
An organization’s whole risk management plan depends heavily on IT Disaster Recovery (IT DR). Ensuring the continuity of operations and thereby reducing the harm caused by unanticipated events, including system failures, cyberattacks, and natural disasters, is the main objective.
Given the criticality of IT systems’ corporate environments, creating and executing a strong IT Disaster Recovery plan is vital.
Let’s explore how the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) framework can provide a structured and comprehensive approach to IT disaster recovery.
Understanding the NIST Framework
The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) framework is a comprehensive set of guidelines and standards designed to improve organizations’ overall cybersecurity posture.
While it encompasses various aspects of cybersecurity, the NIST framework is particularly valuable in the context of IT disaster recovery for its structured and methodical approach.
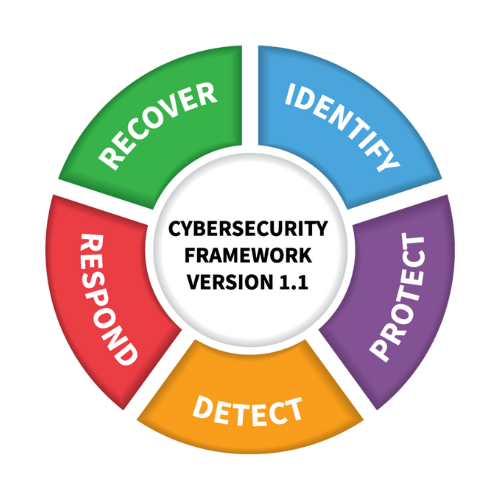
The core components of the NIST framework relevant to IT disaster recovery include:
- Identify: Know and control hazards to systems, assets, data, and capabilities.
- Protect: Implement suitable protections to guarantee the supply of services related to critical infrastructure.
- Detect: Develop activities to identify the occurrence of a cybersecurity event.
- Respond: By creating and carrying out initiatives meant to counteract found cybersecurity incidents.
- Recover: Maintain plans for resilience and restore any capabilities or services impaired during a cybersecurity event.
These elements give a disciplined approach to guaranteeing companies can not only react to but also effectively recover from crises, therefore protecting vital operations and reducing downtime.
Risk Assessment and Management
Building an IT disaster recovery plan starts with a risk assessment. It entails spotting possible hazards, from cyberattacks to natural disasters, that can cause disturbances to IT operations. Good risk control strategies can help reduce these hazards and guarantee the continued running of companies.
Here are some actionable steps for conducting risk assessments based on the NIST framework:
- Identify Assets: Create an inventory of all hardware, software, and data critical to your organization’s operation.
- Identify Threats: Determine potential threats to these assets, such as hardware failure, human error, cyber-attacks, and natural disasters.
- Evaluate Vulnerabilities: Assess the weaknesses in your IT infrastructure that could be exploited by the identified threats.
- Analyze Impact: Evaluate the potential impact of each threat on business operations. This could include financial loss, reputational damage, or loss of data integrity.
- Prioritize Risks: Rank the identified risks based on their potential impact and likelihood of occurrence.
Developing the Disaster Recovery Plan

Developing an effective Disaster Recovery (DR) plan involves creating detailed strategies to restore IT functions promptly after a disruptive event. The following steps are essential components of a comprehensive DR plan, primarily guided by the NIST framework:
- Set Objectives and Goals
To ascertain the reasonable degree of data loss and downtime, clearly define recovery goals including Recovery Time Objectives (RTOs) and Recovery Point Objectives (RPOs). - Establish Roles and Responsibilities
Give team members particular tasks and responsibilities to guarantee responsibility and clarity during a process of catastrophe recovery. - Create a Detailed Recovery Strategy
Create methodical plans for several calamity possibilities. This should cover procedures for data backup, system recovery, and protocols of communication. - Document Key Resources
List and record the main tools needed for disaster recovery, including specifics about backup sites and infrastructure and contact information for both internal and external stakeholders. - Develop Communication Plans
Make sure, both inside the company and with outside partners, there are open channels of contact. This covers pre-made contact lists and messaging templates. - Implement Security Measures
Include cybersecurity elements into the DR strategy to guard against data leaks throughout the healing phase.
Data Backup and Recovery Best Practices
Any IT DR strategy revolves mostly around data backup and recovery. The two most important things are making sure important data is routinely backed up and that a data recovery plan is adequately established.
These are some best practices consistent with the NIST framework:
- Implement regular data backups to ensure that the most recent data is available for recovery. Automated tools can be used to schedule and manage these backups efficiently.
- Store backups in multiple locations, including off-site and cloud-based storage, to protect against site-specific disasters.
- Employ various types of backup solutions, such as full, incremental, and differential backups, to optimize storage and recovery times.
- Regularly test and validate backups to ensure data integrity and usability during recovery. This can involve routine recovery drills to identify and rectify potential issues in the backup process.
- Protect backup data through encryption to ensure confidentiality and mitigate the risk of data breaches.
- Develop detailed recovery procedures for different types of data and systems. These procedures should be accessible to relevant personnel and regularly updated.
Following these best practices can help guarantee strong and dependable data backup and recovery procedures, therefore reducing data loss and downtime during a disaster.
Testing and Maintenance

The effectiveness of a disaster recovery strategy depends on ongoing testing and revisions. Frequent testing guarantees that the strategy stays workable and that every staff member knows their duties and obligations.
These salient features should help you evaluate and keep your IT DR strategy intact:
Regular Checks
The success of a disaster recovery plan depends on how often it is tested and changed. Testing the plan often makes sure that it stays useful and that everyone on staff knows what they need to do.
Plan Regular Drills
Do regular drills for disaster recovery that include different kinds of calamities. This helps find any holes in the plan and gives staff training in real-life situations.
Reviews and Updates
The DR plan should be looked at and changed on a regular basis to keep up with changes in the business, the IT environment, and new threats. If there are big changes in technology or infrastructure, the plan should be looked at again and changed right away.
Involve Stakeholders
Include all important stakeholders in the testing process, such as management, IT staff, and outside vendors, to make sure that all aspects are fully covered.
Post-Test Analysis
Look for ways to improve after each drill by doing a full analysis. Write down what you learned and make any changes that are needed to the DR plan.
Compliance Checks
To make sure the DR plan is in line with regulations and best practices in the business, check it regularly. This can also include audits by a third party to get a fair look at things.
Automated tracking
Use tools for automated tracking to keep an eye on how well the DR plan is working. These tools can give you updates and warnings about possible problems in real time.
By testing and updating the Disaster Response plan on a regular basis, businesses can make sure it works, which reduces downtime and the damage from mishaps.
Thoughts on Technical Planning for Disasters
In order to make sure your systems can handle and recover from all kinds of catastrophes, companies should think about technical contingency planning, which is covered in Chapter 5 of the NIST Special Publication 800-34.
Here are some common considerations that apply across all information system platforms:
- Leverage the Business Impact Analysis (BIA) to determine recovery strategies and priorities.
- Maintain robust data security, integrity, and backup procedures.
- Protect critical hardware, software, and other resources from environmental and component-level failures.
- Adhere to the security controls outlined in NIST SP 800-53 to enhance system resilience.
- Identify alternate storage and processing facilities to support recovery operations.
- Incorporate high availability (HA) processes to maximize system uptime.
When it comes down to it, resilient information systems that can endure and recover from all sorts of interruptions require good technological backup plans. An organization’s capacity to keep vital processes running and to deal with unforeseen events can be strengthened by applying these factors.
The Role of Managed Detection & Response (MDR) in Disaster Recovery
Managed Detection and Response (MDR) services can play an important role in IT disaster recovery and contingency planning.
MDR providers can assist with the rapid detection, analysis, and containment of cyber incidents during a disruption or disaster.
Their threat hunting capabilities and 24/7 monitoring can help identify and mitigate threats quickly, reducing the impact on IT operations.
MDR teams can help ensure that critical data backups are secure and accessible for restoration during recovery efforts and can provide guidance on backup strategies, testing, and validation to improve the reliability of the data recovery.
By integrating MDR services into the overall IT disaster recovery and contingency planning strategy, organizations can leverage the specialized capabilities and 24/7 support to enhance their resilience and ability to recover from disruptive events. The combination of proactive threat detection, incident response, and recovery assistance can be a valuable asset in maintaining business continuity during challenging times.