German healthcare sector providers having to cope with a shortage of qualified security operations (SecOpS) talent could not have happened at a worse time.

However, this modernization also creates more cybersecurity vulnerabilities and air gaps. With these new digital health technologies, the entire healthcare German market will face additional complex cyberattacks and increased attack velocities. A shortage of security talent will hinder the ability of these transformations to become fully operational.

Are you a healthcare provider seeking a solution for IT staff shortages? Click here to schedule an initial consultation with the ForeNova healthcare security team today!
What are the Immediate Benefits German Healthcare Providers Receive from MDR?
German healthcare providers who want to strengthen their security, reduce costs, and prepare for cyberattacks will immediately see positive results from leveraging an MDR service.
These benefits include:
Access to Advanced Cybersecurity Tools
MDR providers invest in the latest advanced technologies for endpoint security, security event information management (SIEM), and incident response automation functionality. Healthcare providers lacking SecOps engineer talent to test, evaluate, and support these tools will gain access to them as they become available through the MDR service offerings.
Scaling up Automated Incident Resources
Managed security service providers (MSSP) and MDR providers have access to global resource talent, extending their ability to scale up their cloud-based services to handle far more incident response events than most small-medium-enterprise (SME) healthcare providers. This benefit helps reduce operational costs and increase SecOps efficiencies by leveraging proven experts in SecOps from ForeNova.
Phase-out legacy on-premises security products

The hospital’s cost for sustaining these standalone security layers, including hiring security engineers with the experience to manage them, continues to increase yearly. When acquiring these solutions, the hospital opted for long-term, perpetual license agreements instead of subscription-based models. Despite many outdated or technically obsolete devices, the hospital had to renew its maintenance contracts.
Many of these tools came with various medical devices or applications. They also added a layer of duplication for security protection, making the security operations far more complicated and expensive.
Moving forward with an MDR offering from ForeNova allows the health organization to phase out expensive and less effective cybersecurity tools.
Greater Access to Threat Intelligence Data
MDR providers can access more security telemetry information than most German health organizations. ForeNova collects and learns from the telemetry information by processing data through its large language models (LLM) within its artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) engines. Combined with threat intelligence, these engines optimize ForeNova’s MDR automated incident response capabilities.
Other MDR offerings charge their clients for access to the Threat Intelligence data. ForeNova understands the financial challenges SMEs in German healthcare face. The company supports many SMEs with its pricing model, which includes bundling several services under one price point.
More Robust Support for NIS, Patient Data Protection (PDSG), and GDPR Compliance
Like the U.S., Germany’s healthcare industry has several compliance mandates that must be completed and sustained. These mandates, including NIS2, GDPR, and PDSG, all require similar cybersecurity protection layers, continuous monitoring, automated incident response, robust reporting and notification, and enablement of the cybersecurity adaptive controls commonly available throughout the German health service.
MDR helps German health providers meet their compliance requirements.
Reduce Downtown and Operational Disruptions
Another critical benefit healthcare providers gain from leveraging MDR is the reduction of downtown and production system effects caused by a cyberattack.
MDR providers also support their clients as security architecture and solutions recommendations specialists. Integrated health organizations are extending their supply chain, adding Internet-of-Things (IoT) medical devices, or expanding the ability for doctors to access response services at a remote clinic remotely. With the constant change in the global threat landscape, hackers can breach these new medical business operations after deployment. MDR providers can make recommendations and assist in the implementation before the new medical functions become operational.
This decision helps the German medical provider reduce the downtown of the various digital assets, patient record systems, and operating room equipment.
Challenges When Enabling MDR Solutions
MDR offers considerable benefits, including reducing cyber threats through proactive threat hunting, reducing alert fatigue of their current staff, and leveraging advanced analytics for faster incident response.
Yet, even with these success factors, enabling MDR capabilities is challenging.
MDR is a subscription service that requires the German medical firm to contract with a provider like ForeNova to leverage its services. SME medical providers may need more money to use this cybersecurity service. Another challenge is resistance to change. Members of the existing internal IT and security teams recognize that outsourcing their daily functions could affect their job status. This resistance element often prevents many outsourced cybersecurity services from becoming fully functional.
Another challenge with MDR offerings is working with legacy security tools. Legacy email security tools, endpoint solutions, and log collection functions may have capability issues with the MDR solution.
A critical part of the MDR journey mandates that the healthcare provider and the MDR service providers collaborate to conduct pre-deployment assessments and decide which existing security solutions should be replaced or moved to the out-of-scope bucket.
What is the cost of MDR compared to staffing in in-house SecOps?
Healthcare providers moving from an in-house security operations center to an MDR provider extends several cost savings opportunities.
- Phasing out existing cybersecurity solutions and canceling unused subscriptions.
- Recreating updated security policies and phasing out obsolete IT and security operations procedures.
- Re-purposing internal IT and cybersecurity resources for more strategic roles.
- There is no immediate need to update existing security infrastructure if these controls become part of the MDR offering.
Here is an example of a cost-savings model German healthcare providers can use as a financial guideline:
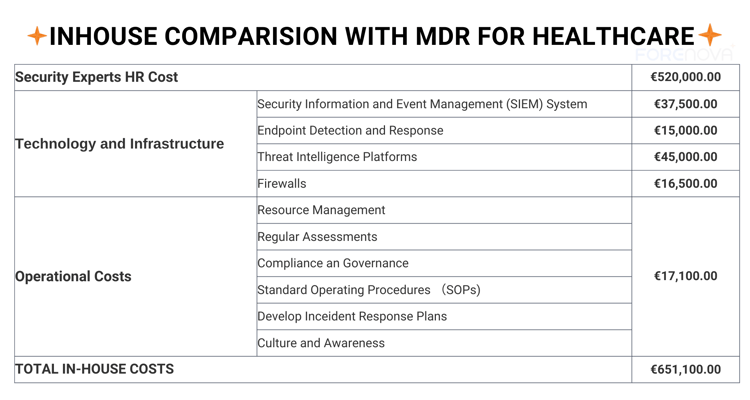
Considerations
German healthcare providers evaluating an MDR service compared to their current in-house SecOps strategy need to consider:
- The cost of security engineers and the availability of experienced talent will always be a challenge.
- Healthcare providers will need to invest in continuous updates of new cybersecurity technology, training, and double pay for a few months while the legacy solutions are replaced.
- Healthcare organizations must invest in continuous updates of new cybersecurity technology and training and pay double for a few months while they replace legacy solutions.
- Healthcare providers will need to continue investing in engineering talent training and development and taking further steps to ensure these trained resources remain with the organization.
What Efficiencies Will Healthcare Providers Gain By Leveraging MDR Services?
Choosing to leverage an MDR offering delivers exceptional efficiencies for a health organization. These efficiencies represent a short list available for healthcare providers:
- Develop and sustain consistency in SecOps procedures and the ability to respond to sophisticated cyberattacks.
- Sustain a high-security posture status consistently.
- Remain a high state compliance readiness throughout the business year.
- Reduce the security operations to a predictable level with a fixed expense.
- The ability to scale up cybersecurity resources with high accuracy.
- Reduction of capital expenditures for security infrastructure
- Gain peace of mind regarding cyber response, compliance readiness, and reporting.
What Components Comprise an MDR Offering?
MDR offerings leverage several technology controls, coverage models, and engagements. Most MDR offerings focus on the core services, including:
- 24 x 7 monitoring
- Automated incident response
- Reporting for compliance notifications
- Threat modeling
- Access to Threat Intelligence
Additional services available for German health organizations include:
- Staff augment to support existing internal SecOps
- Enable endpoint security solutions
Why ForeNova?
Working with an experienced MDR provider like ForeNova is critical for all German Healthcare organizations that must address staffing challenges, meet compliance deadlines, and respond to more cyberattacks. ForeNova’s expertise in MDR services, along with its security architecture background, makes it an invaluable partner for the health sector in Germany and the rest of the EU.
Click here to schedule your first demonstration today with the ForeNova team


 Healthcare organizations in Germany must follow several compliance mandates to protect their critical infrastructure. HIPAA for Germany, GDPR, and the German Federal Data Protection Act.
Healthcare organizations in Germany must follow several compliance mandates to protect their critical infrastructure. HIPAA for Germany, GDPR, and the German Federal Data Protection Act.




